Deep Neural Networks
文中部分图片截取自课程视频Nerual Networks and Deep Learning
Now we have a better understanding of how the two-layer neural networks works, we can apply and extend the idea to any multi-layer neural network.
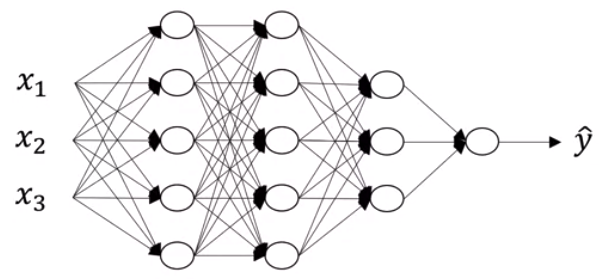
Notations
- $n^{[l]}$: #units in layer $l$
- $a^{[l]}$: #activations units in layer $l$
- $a^{[l]}=g^{[l]}(z^{[l]})$
- $a^{[0]} = X$
- $W^{[l]}$: weights for $z^{[l]}$
- $b^{[l]}$: bias vector
Forward Propagation for Layer $l$
- Input $a^{[l-1]}$
- Output $a^{[l]}$, cache (z^{[l]})
其中,$W^{[l]}$矩阵的维度为$(n^{[l]}, n^{[l-1]})$, $b^{[l]}$的维度为$(n^{[l]},1)$,$Z^{[l]}$和$A^{[l]}$均为$(n^{[l]},m)$ (m为训练样本数量)
Although we can use vectorization to compute $A^{[l]}$ more easily, we still need to use a explicit for-loop to loop thourgh all the hidden layers, as the deep neural networks always have more than one layers.
Backward Propagation for layer $l$
- Input $da^{[l]}$
- Output $da^{[l-1]}$, $dW^{[l]}$, $db^{[l]}$
- Vetorized version
Hyperparameters
- learning rate $\alpha$
- #iterations
- #hidden layer
- #hidden units
- choice of activation function
- …
Build a Multilayer Neural Networks in Numpy
和前一篇文章类似,接下来我们将用numpy来实现一个L层的神经网络。我们另前$L-1$层的Activation函数为Relu,最后一层的Activation函数为Sigmoid。
- Initialization
def initialize_parameters_deep(layer_dims):
"""
Arguments:
layer_dims -- python array (list) containing the dimensions of each layer in our network
Returns:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters "W1", "b1", ..., "WL", "bL":
Wl -- weight matrix of shape (layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1])
bl -- bias vector of shape (layer_dims[l], 1)
"""
np.random.seed(3)
parameters = {}
L = len(layer_dims) # number of layers in the network
for l in range(1, L):
parameters['W' + str(l)] = np.random.rand(layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1]) * 0.01
parameters['b' + str(l)] = np.zeros((layer_dims[l], 1))
return parameters
参数初始化完成后,我们可以来实现FP了,借助前一篇两层神经网络的linear_forward和linear_activation_forward函数,我们可以方便的实现第$L$层的forward
def L_model_forward(X, parameters):
"""
Implement forward propagation for the [LINEAR->RELU]*(L-1)->LINEAR->SIGMOID computation
Arguments:
X -- data, numpy array of shape (input size, number of examples)
parameters -- output of initialize_parameters_deep()
Returns:
AL -- last post-activation value
caches -- list of caches containing:
every cache of linear_activation_forward() (there are L-1 of them, indexed from 0 to L-1)
"""
caches = []
A = X
L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network
# Implement [LINEAR -> RELU]*(L-1). Add "cache" to the "caches" list.
for l in range(1, L):
A_prev = A
A, cache = linear_activation_forward(A_prev, parameters["W"+str(l)], parameters["b"+str(l)], "relu")
caches.append(cache)
# Implement LINEAR -> SIGMOID. Add "cache" to the "caches" list.
AL, cache = linear_activation_forward(A, parameters["W"+str(L)], parameters["b"+str(L)], "sigmoid")
caches.append(cache)
assert(AL.shape == (1,X.shape[1]))
return AL, caches
- Cost Function
回顾计算Cost函数的公式如下
\[-\frac{1}{m} \sum\limits_{i = 1}^{m} (y^{(i)}\log\left(a^{[L] (i)}\right) + (1-y^{(i)})\log\left(1- a^{[L](i)}\right)) \tag{7}\]def compute_cost(AL, Y):
"""
Implement the cost function defined by equation (7).
Arguments:
AL -- probability vector corresponding to your label predictions, shape (1, number of examples)
Y -- true "label" vector (for example: containing 0 if non-cat, 1 if cat), shape (1, number of examples)
Returns:
cost -- cross-entropy cost
"""
m = Y.shape[1]
# Compute loss from aL and y.
cost = -1/m *(np.dot(Y, np.log(AL.T)) + np.dot(1-Y, np.log(1-AL).T))
# To make sure your cost's shape is what we expect (e.g. this turns [[17]] into 17).
cost = np.squeeze(cost)
assert(cost.shape == ())
return cost
- Backward propagation
上面我们通过了L_model_forward对每层进行FB运算,并且缓存了(X,W,b, and z)。接下来我们便可以用这些缓存的结果进行反向求导。我们知道最后一层的输出结果为$A^{[L]} = \sigma(Z^{[L]})$,因此我们首先需要计算的是 $= \frac{\partial \mathcal{L}}{\partial A^{[L]}}$
# derivative of cost with respect to AL
dAL = - (np.divide(Y, AL) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - AL))
接下来我们便可以使用dAL对sigmoid函数求导得出$dW^{[l]}$,$db^{[l]}$,$dA^{[l-1]}$,接下来通过一个for循环,逐层求解$dw$,$db$和$dA$,如下图所示
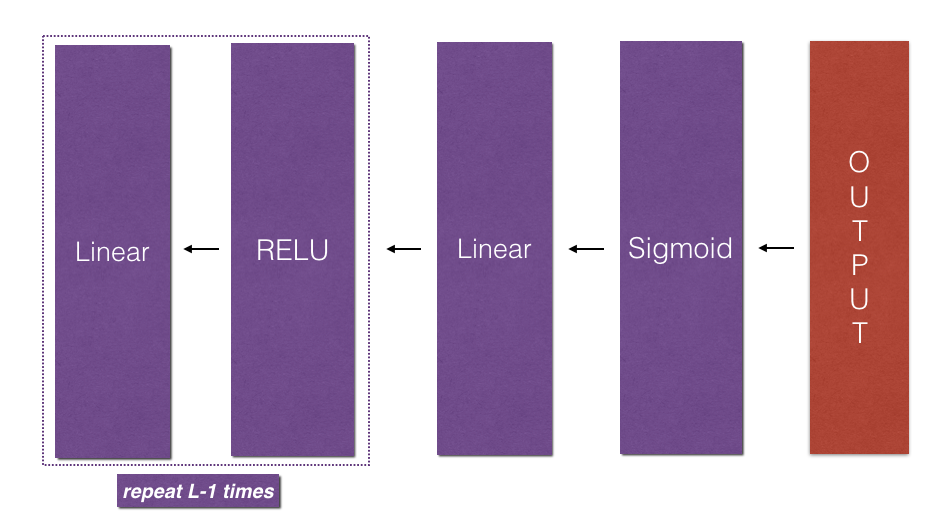
在反向求导的过程中,我们需要将dA,dW和db缓存起来,便于后续梯度下降运算
def L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches):
"""
Implement the backward propagation for the [LINEAR->RELU] * (L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID group
Arguments:
AL -- probability vector, output of the forward propagation (L_model_forward())
Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if non-cat, 1 if cat)
caches -- list of caches containing:
every cache of linear_activation_forward() with "relu" (it's caches[l], for l in range(L-1) i.e l = 0...L-2)
the cache of linear_activation_forward() with "sigmoid" (it's caches[L-1])
Returns:
grads -- A dictionary with the gradients
grads["dA" + str(l)] = ...
grads["dW" + str(l)] = ...
grads["db" + str(l)] = ...
"""
grads = {}
L = len(caches) # the number of layers
m = AL.shape[1]
Y = Y.reshape(AL.shape) # after this line, Y is the same shape as AL
# Initializing the backpropagation
dAL = - (np.divide(Y, AL) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - AL))
# Lth layer (SIGMOID -> LINEAR) gradients. Inputs: "dAL, current_cache". Outputs: "grads["dAL-1"], grads["dWL"], grads["dbL"]
current_cache = caches[L-1]
grads["dA" + str(L-1)], grads["dW" + str(L)], grads["db" + str(L)] = linear_activation_backward(dAL, current_cache, activation = "sigmoid")
# Loop from l=L-2 to l=0
for l in reversed(range(L-1)):
# lth layer: (RELU -> LINEAR) gradients.
# Inputs: "grads["dA" + str(l + 1)], current_cache". Outputs: "grads["dA" + str(l)] , grads["dW" + str(l + 1)] , grads["db" + str(l + 1)]
current_cache = caches[l]
dA_prev_temp, dW_temp, db_temp = linear_activation_backward(grads["dA" + str(l+1)], current_cache, activation = "relu")
grads["dA" + str(l)] = dA_prev_temp
grads["dW" + str(l + 1)] = dW_temp
grads["db" + str(l + 1)] = db_temp
return grads
- Update Parameters
在每次BP完成后,我们需要对$dw$h和$db$进行梯度下降
\[\begin{align*} & W^{[l]} = W^{[l]} - \alpha \text{ } dW^{[l]} \\ & b^{[l]} = b^{[l]} - \alpha \text{ } db^{[l]} \end{align*}\]
def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate):
"""
Update parameters using gradient descent
Arguments:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters
grads -- python dictionary containing your gradients, output of L_model_backward
Returns:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your updated parameters
parameters["W" + str(l)] = ...
parameters["b" + str(l)] = ...
"""
L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network
# Update rule for each parameter. Use a for loop.
for l in range(L):
parameters["W" + str(l+1)] = parameters["W" + str(l+1)] - learning_rate * grads["dW"+str(l+1)]
parameters["b" + str(l+1)] = parameters["b" + str(l+1)] - learning_rate * grads["db"+str(l+1)]
return parameters
