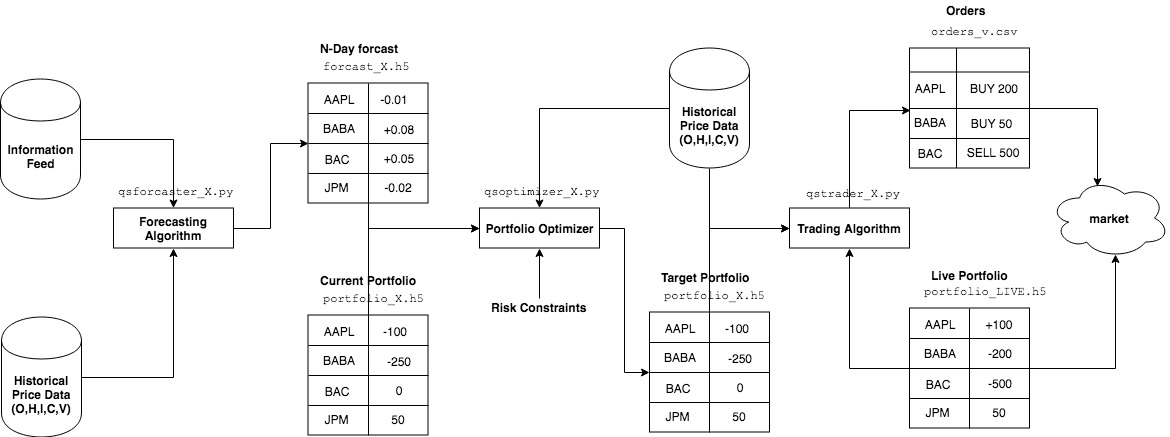
资产组合与市场机制
Online course from Coursera & Udacity
Portfolio Management
- Expense ratio
- Used by mutual funds & ETFs
- Usually less than 1%
- “Two and twenty”
- Classic structure for hedge funds.
- 2% of assets under management + 20% of the returns.
- 1M with 20% per year = 60k per year
- How/Why different?
- 共同基金或者ETF基金经理目标是增大基金数额来赚取管理费
- 私募基金或者对冲基金经理目标是提高基金收益
How to Attract Investors
- 资金来源
- Individuals
- 个人投资者,资金占比较少
- Institusions
- 机构投资者
- Harvard Foundation
- CalPERS
- 机构投资者
- Funds of Funds
- 来自其他基金的投资
- Individuals
- Two Main Types of Fund Goals
- Reference to a benchmark
- 有指标参考,比如跑赢S&P500等
- Absolute return
- 低风险策略,只关注收益回报
- Reference to a benchmark
Metrics for Assessing Fund Performance
- Common Metrics
- Annual Return
- metric:
(value[end] / value[star])) -1(value[end] - value[start])/value[start]
- Example: $100 to $110
(110/100) -1 = 0.1 = 10%(110-100)/100 = 0.1 = 10%
- metric:
- Risk
- 定义风险:Standard deviation of return
- daily return
//日回报保准差 daily_rets[i] = (value[i]/value[i-1]) -1 std_metrics = stdev(daily_rets) - Draw down
- 最大跌幅
- 平均跌幅
- 定义风险:Standard deviation of return
- Annual Return
- Reward/Risk
- 收益风险比,How much reward you are getting for your risk?
- Sharpe Ratio
- Most “important” measure of asset performance.
- How well does the return of an asset compensate the investor for the risk taken
- The higher the Sharpe ratio the better.
- When comparing two assets each with the same return, higher ratio gives more return for the same risk.
-
seudo code
metric = k * mean(daily_rets)/stdev(daily_rets) # k = sqrt(250) for daily returns # 250: days in a trading year
- Sortino Ratio
- Sortino ratio only penalizes for negative volatility in the calculation of risk.
- Sharpe ratio penalizes for both positive and negative volatility.
- Jensen’s Alpha
- Example
假设有一只Fund,它参考Dow Jones指数的benchmark如下:
| Return | Sharpe | STDEV | D-down | Corr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xxFund | 33% | .94 | 0.58% | -8.67% | 0.89 |
| $DJI | 43% | .63 | 1.23% | -27.38% | 1.00 |
- 该基金没有收益率没有跑赢大盘,但是Sharpe指数高于大盘,说明它的整体波动率较低,相对于收益的风险更小
- 同样,STDEV,D-down 数据也偏低,说明日均波动较小
Market Mechanics
- Types of Orders
- But,Sell
- Market, Limit
- Shares
- Price(if Limit)
- Additional possibilities:
- Sell short
- More complex orders
- The Order Book(买盘与卖盘)
- Ask (Buy)
- Bid (Sell)
- Mechanics of Short Selling
- Borrow the shares 像券商融券
- 立刻卖掉融到的券
- 拿到现金
- 需要在未来归还券商融到的股票
- 如果价格未来价格下跌
- 只需要支付较低价格来买回股票还给券商
- 差价即是利润
Computing Inside a Hedge Fund
Company Worth
- Key Terms
- 使用贴现率
假设我们今天有
- 使用折现率
假设我们投资一家公司,这个公司每年一股能产生1美金的利润(dividend),那么我们现在应该以每股多少钱购入它的股票?换句话说,这个公司现在每股的价值该怎么计算,或者说这个公司的固执该怎么计算呢?为了比较,假设我们也可以把买这家公司股票的前钱存到银行,同样每年能赚取1美金。假设银行的利息是1分钱,那么我们需要向银行存入0.99美元,一年后能拿到1块钱。对于公司来说,它承担的风险比银行高,因此它的收益也比银行高,假设我们只需要投资0.95美元一年后即可得到1块钱收益。这意味着
一年后1美元利润,现在只值0.95美元。而0.95/1这个比例值也叫做这个折现率(discount rate)
|now |year1 |year2 |year3
Company ----> $1.00 ----> $1.00 ---->$1.00 --->...
$0.95
Bank -----> $1.00 ----> $1.00 ---->$1.00 --->...
$0.99
注意,上面提到的折现率不仅仅是针对的一年的,而是无限长时间内的,而时间越长,1美元折现的价值越低, 如果过了几百年,1美元折现到现在基本上约等于0。这也意味着一家每年固定利润为1美金的公司,随着时间的增长,它的估值并不是无穷大的,因为未来的1美金对于现在来说,基本上就等于0
--->0.95---->0.95^2----->0.95^3......-->~0.0
|year1 |year2 |year3 |year n
我们可以通过折现率用下面公式计算一家公司的估值
\[Value=Sum(dividen*gamma^i) = \sum_{i=1}^\infty dividen * gamma^i = {dividend * 1}/{(1-gamma)}\]其中$dividen$表示公司的每股利润(股息),$gamma$表示折现率,上面例子中,这家公司的估值为20美金
\[Value=\sum_{i=1}^\infty 1.00 * 0.95^i=\frac{1.00}{(1-0.95)}=20.00\]- Book Value
- 净资产
- “Total” assets minus intangible assets and liabilities.
综上所述,公司的价值为:未来估值+净资产。另一种更直观的计算方式为:#(outstanding shares) * price 即流通股数 * 股票价格
CAPM
CAPM是Capital Assets Pricing Model的缩写,翻译过来叫做资本资产定价模型。1966年由Jack Treynor, William Sharpe, John Linter和Jan Mossin共同提出,其中Sharpe,Markowitz和Merton Miller还因此共同获得了诺奖。这个理论的提出,改变了当时人们对投资的理念,基于这个模型和有效市场假说,有观点认为投资指数基金或者配置资产来跟踪指数是比较好的选择,也就是所谓的被动投资。
本课程的投资观点(量化交易)是一种主动投资的理念,Tucker Balch指出基于这种理念也可以取得不错的汇报,但是CAPM模型影响力非常大,是各种投资产管理理论的基础,因此有必要仔细了解
- CAPM假说
- Return of stock has two components:
- Systematic (the market)
- Residual
- Expected Value of residual = 0
- Market return
- Risk free rate of return + Excess return
- Return of stock has two components:

上图为BABA和NASDAQ近三个月的走势叠加图, 可以看到大部分时间BABA和NASDQ的走势基本持平。波动的部分则为BABA自身的股价变化。CAPM认为股价由两方面决定, 一方面市场波动,一方面是个股波动。他们之间的关系为
\[\gamma_i=\beta_i * \gamma_m + \alpha_i\]$\gamma_i$表示股价,它的值为市场波动系数$\beta_i$乘以前一天的价格加上个股当天波动的价格$\alpha_i$。按照CAPM理论,在大部分时间内,某家公司的股价应该随着指数的波动而波动,即$\alpha_i$的期望为0,而如果表现出偏离,则说明这家公司具备某些可以挖掘的信息。
Resources
附 Install QSTK on MacOS
官方指南 有些步骤已经过时,这里整理一份暂时可用的,测试通过了
\Examples\Basics\下的所有tutorial.py,环境为Python2.7
- Install Pip
brew install python
pip install --upgrade setuptools
pip install --upgrade pip
- Install virtualenv
pip install nose
pip install virtualenv
- Install Numpy, Scipy and Matplotlib
这些库依赖gfortran,后者在brew库中已经被移到gcc,因此这里brew install gfortran会失败,可以用gcc替代:
brew install gcc
如果在执行make时卡住,尝试更新XCode插件sudo xcode-select --install。
安装GCC成功后,还需要先更新home brew的两个Science库:
brew tap brewsci/homebrew-science
brew tap brewsci/bio
然后安装 Numpy, Scipy and Matplotlib
brew install numpy
brew install scipy
brew install matplotlib
- 创建一个QSTK的测试目录
mkdir ~/QSTK
cd ~/QSTK
- 使用virtualenv进行环境隔离
virtualenv env --distribute --system-site-packages
source ~/QSTK/env/bin/activate
activate之后的安装都将与全局环境隔离,这里要先check一下env/lib/下的python版本, 如果误使用了python3,要还原回来,需要重新指定python版本
virtualenv --python=/usr/bin/python2.7 ~/QSTK/env
- 安装QSTK及其依赖
pip install pandas
pip install scikits.statsmodels
pip install scikit-learn
pip install cvxopt
pip install QSTK
创建matplotlib配置文件:echo "backend: TkAgg" > ~/.matplotlib/matplotlibrc
- 测试QSTK demo
curl -O https://spark-public.s3.amazonaws.com/compinvesting1/QSTK-Setups/Examples.zip
unzip Examples.zip
使用Examples目录中的Validation.py进行测试,如果发现TimeSeries类找不到:
2.7.14_3/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/lib/python2.7/site-packages/QSTK/qstkutil/qsdateutil.py", line 36, in _cache_dates
return pd.TimeSeries(index=dates, data=dates)
AttributeError: 'module' object has no attribute 'TimeSeries'
原因是panda版本过新,还原到0.7.3版本
pip install pandas==0.7.3
- 测试
Basic下的一系列tutorial.py
python tutorial1.py
如果发现
numpy TypeError: The numpy boolean negative, the `-` operator, is not supported, use the `~` operator or the logical_not function instead.
则表示numpy的版本不对,具体是哪个版本还不清楚,暂时的解法是按照提示去出错的地方,修改代码。上述步骤完成后,测试tutorial1.py,成功后可发现Basics目录下生成了多个pdf文件
- 退出
virtutalen环境
/bin/deactive
- 卸载QSTK
rm -rf ~/QSTK