Assembly Lanugage and Computer Architecture
The Four Stages of Compilation
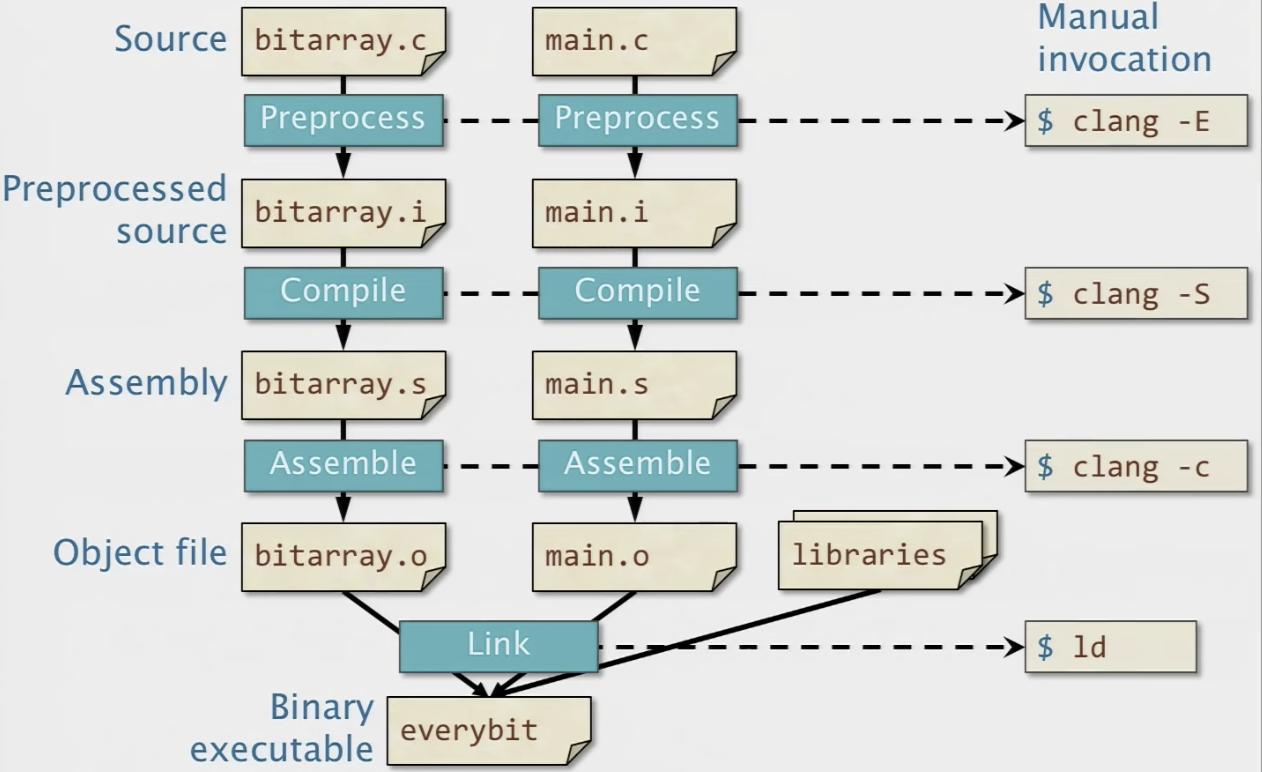
Source Code to Assembly Code
Assembly language provies a convenient symbolic representation of machine code.
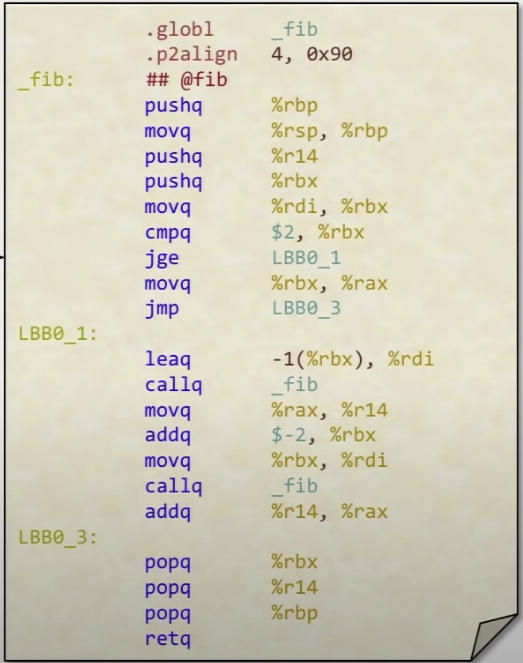
int64_t fib(int64_t n){
if(n < 2){
return n;
}
return (fib(n-1) + fib(n-2));
}
We can do clang -03 fib.c -S to generate the assembly code, which gives the code like this
From here, we assemble the assembly code to produce the binary.
$clang fib.s -o -fib.o
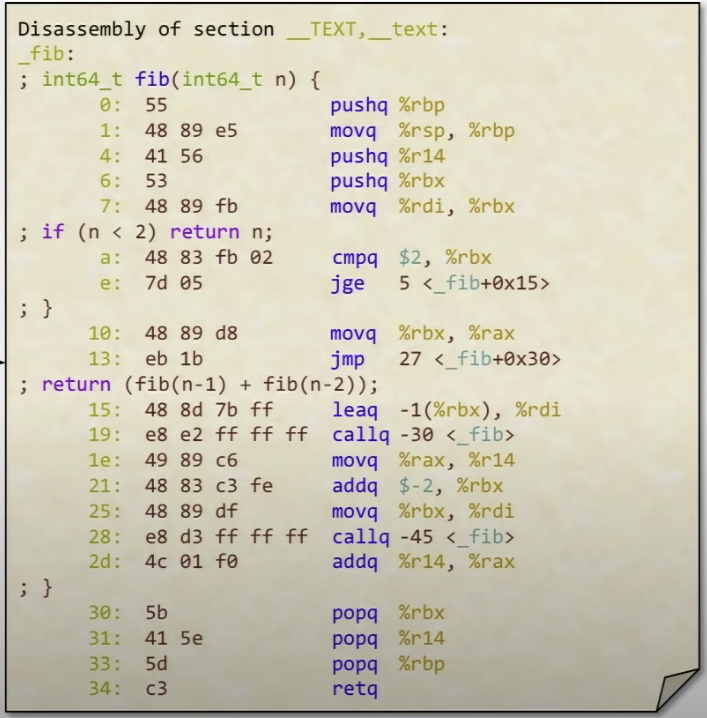
Binary executable produced with debug symbols (compiled with -g) can be dumped using
$objcdump -S fib
This will produce the disassembly of the machine code, which is more readable.
Why Assembly?
Why botter looking at the assembly of your program?
- The assembly reveals what the compiler did and did not do.
- Bugs can arise at a low level. For example, a bug in the code might only have an effect when compiling at
–O3. Furthermore, sometimes the compiler is the source of the bug! - You can modify the assembly by hand, when all else fails.
- Reverse engineering: You can decipher what aprogram does when you only have access to its binary.
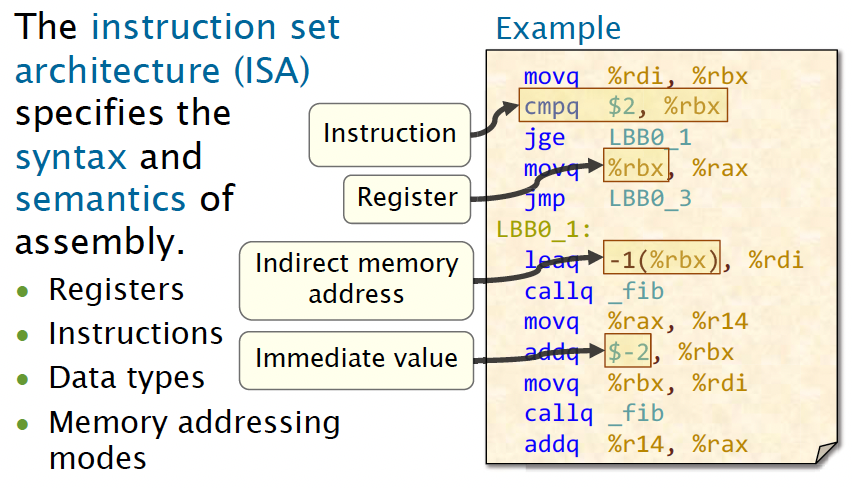
X86-64 Instruction Set Architecture Primer
The instruction set architecture (ISA) specifies the syntax and semenatics of assemebly, which includes Registers, Instructions, Data types and Memory addressing modes.
There are a bunch of x86-64 registers. The important ones are
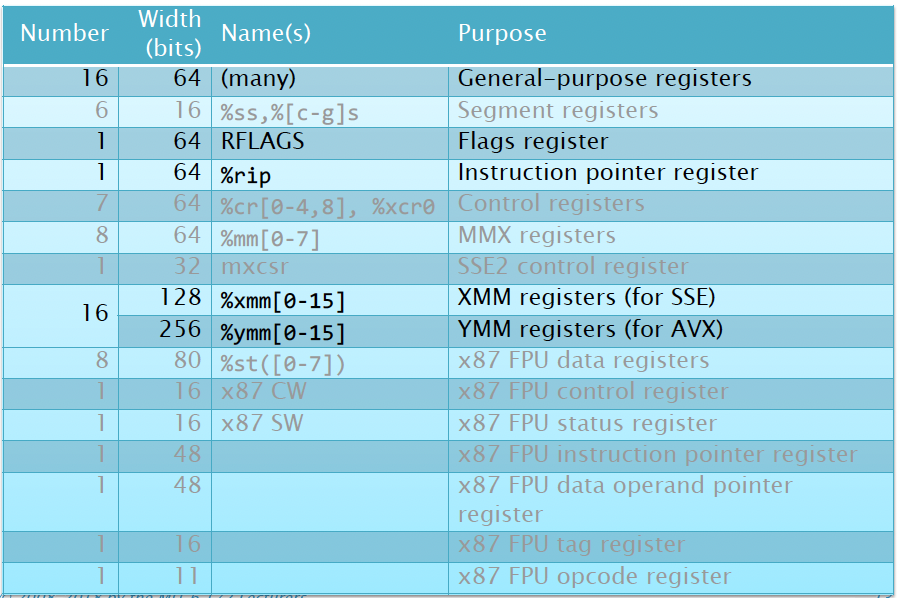
- The Flags register keeps tracking of whether there is a overflow. Or whether the last operation returns 0, etc.
- The instruction pointer register
- The SSE and AVX registers are recently added.These are vector register for SIMD instructions.
The x86-64 general-purpose registers are aliased: each has multiple names, which refer to overlapping bytes in the register.
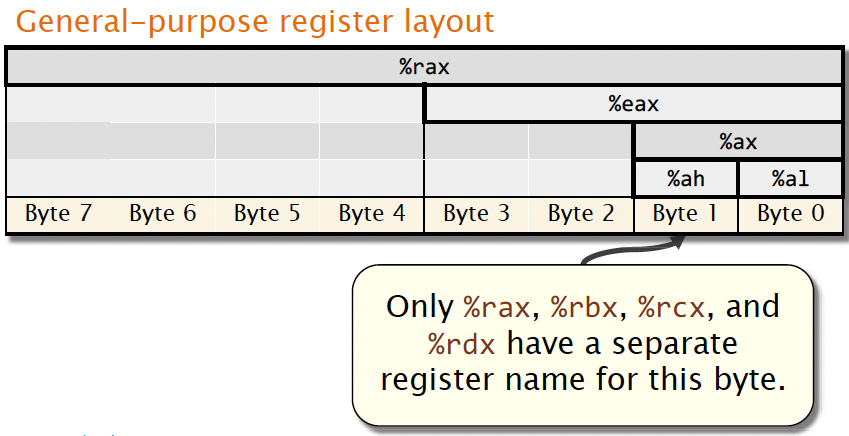
Here are all the general purpose regiesters
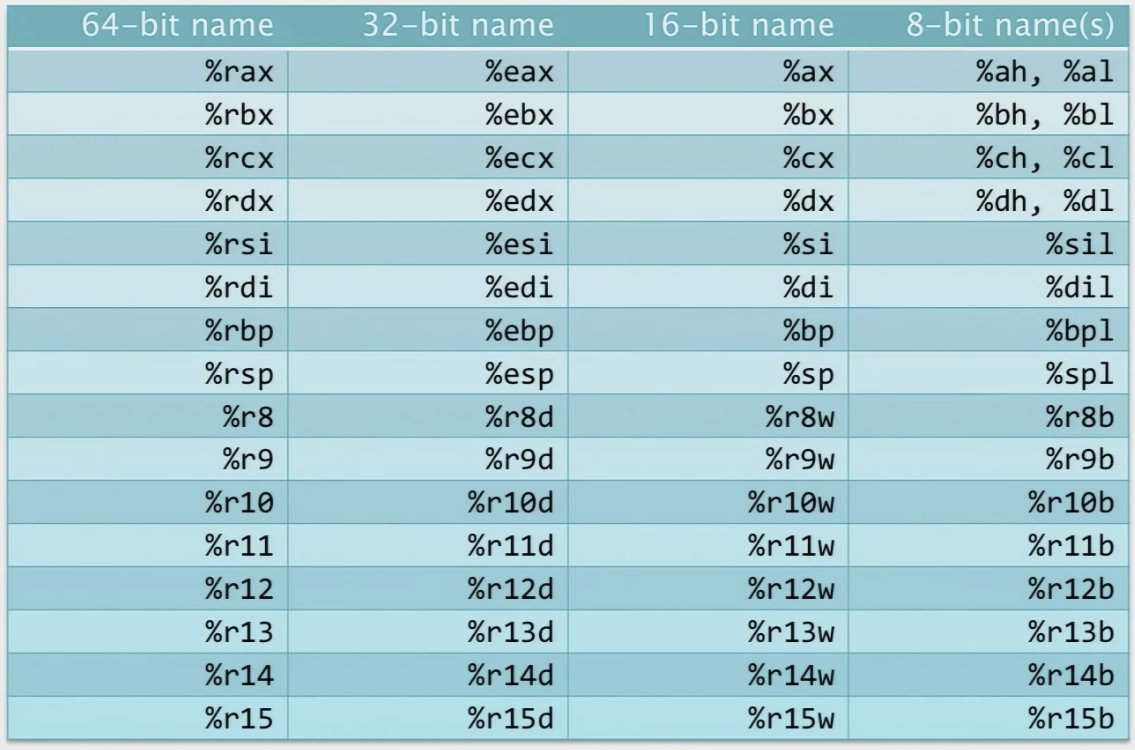
Some of them are still useful for a particular purpose, such as rsp is used as stack pointer, and rbp is used to point to the base of the frame.
The x86-64 Instruction Format
Format: <opcode> <operand_list>
<opcode>is a short mnemonic identifying the type of instruction<operand_list>is 0,1,2 or (rarely) 3 operands, seperated by commas.- Typically, all oeprands are sources, and one operand might also be the destiniation.
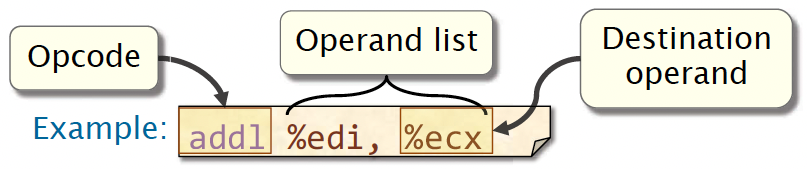
What does <op> A, B mean? There are two syntax standards namely AT&T Syntax and Intel Syntax. In the AT&T syntax, the second operand is the destination, whereas in the Intel syntax, the first operand is the destination.
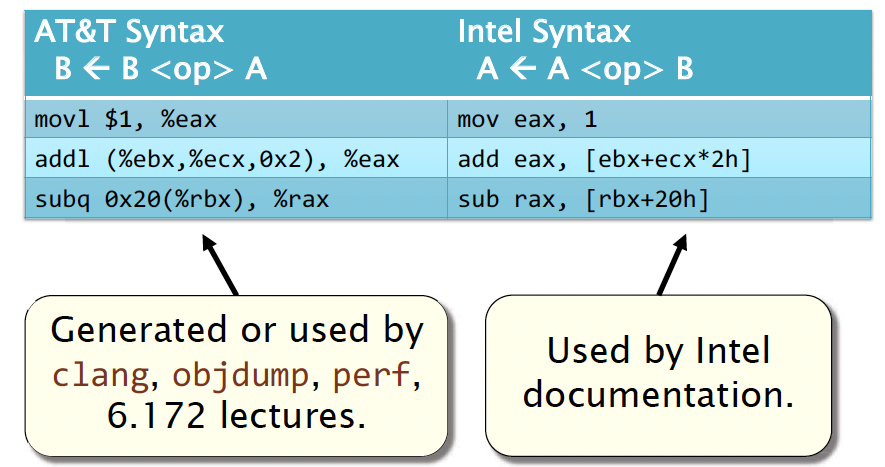
The common x86-64 Opcodes
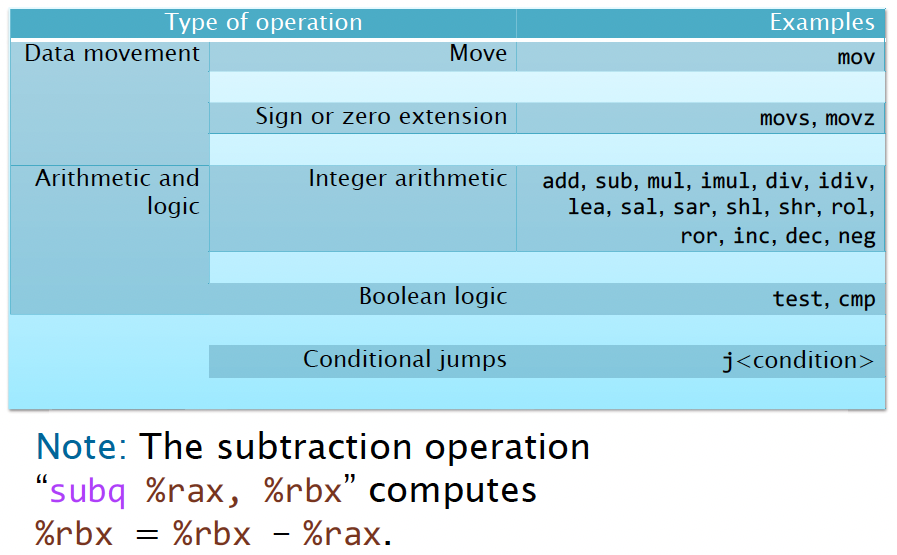
Opcodes might be augmented with a suffix that describes the data type of the operation or a condition code.
- An opcode for data movement, arithmetic or logic uses a single-char suffix to inidicate the data type
- If the suffix is missing, it can usually be inferred from the sizes of the operand registers.

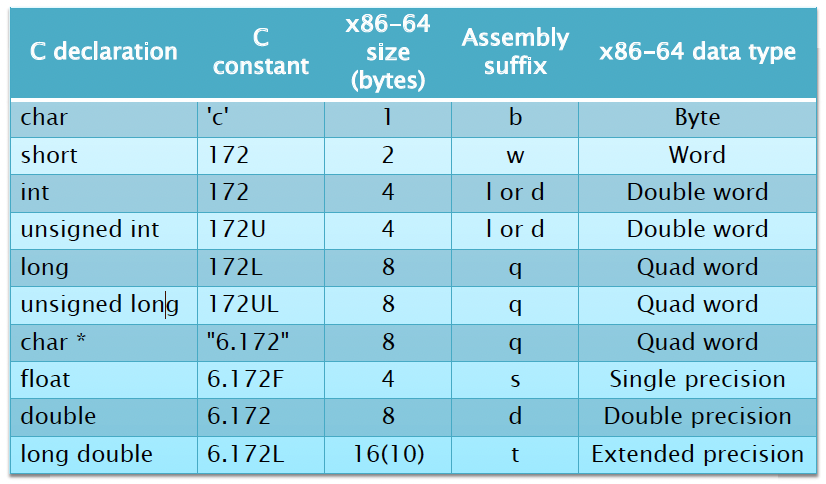
x86-64 Data Types
Conditional Operations
Condiional jumps and conditional moves use a one or two char suffix to indicate the condition code.
cmpq $4096, %r14
jne .LBB1_1
In the example above, ne means the jump should only be taken if the argumetns of the previous comparision are not equal. The previous comparision result is stored in the RFLAG register.
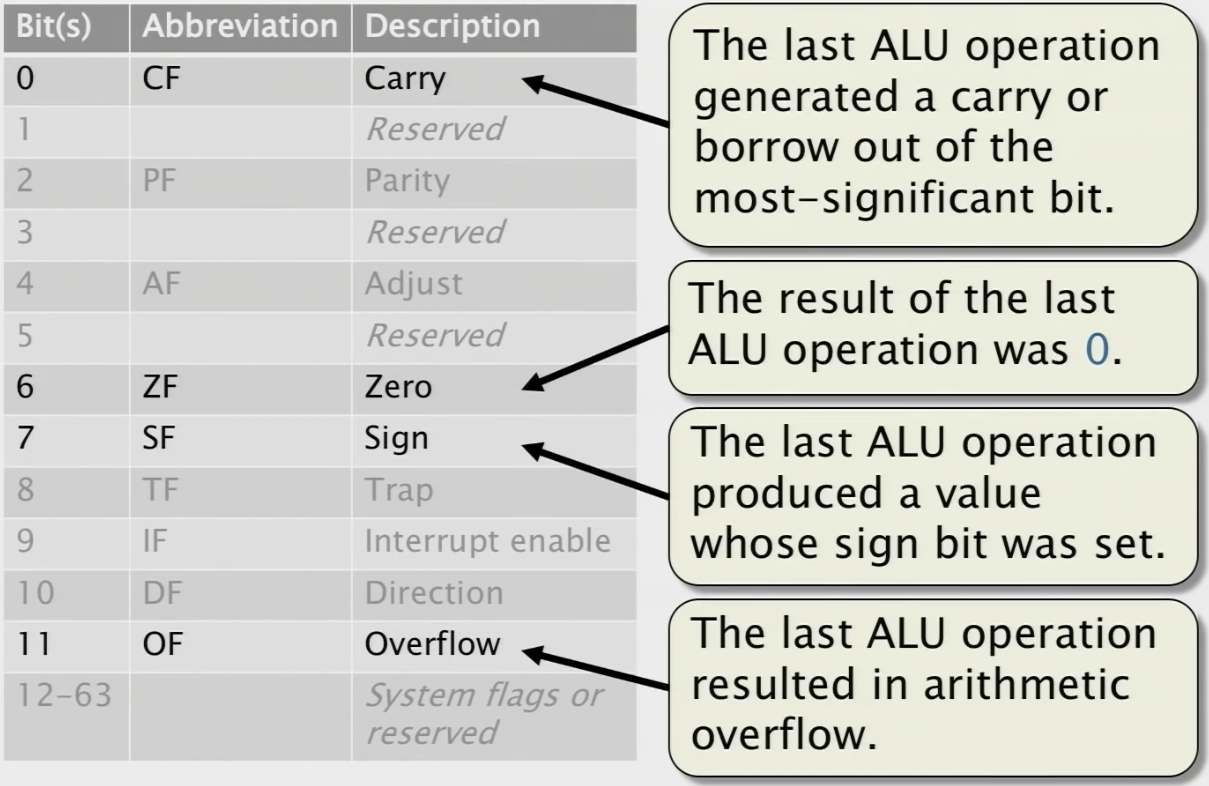
RFLAGS Register
Arithmetic and logic operations update status flags in the RFLAGS register. Common RFLAGS register meanings are listed below
Let take a look at an example
decq %rbx // Decremetn %rbx, and set ZF if the result is 0.
jne .LBB7_1 // Jump to the label .LBB7_1 if ZF is not set
Condition Codes
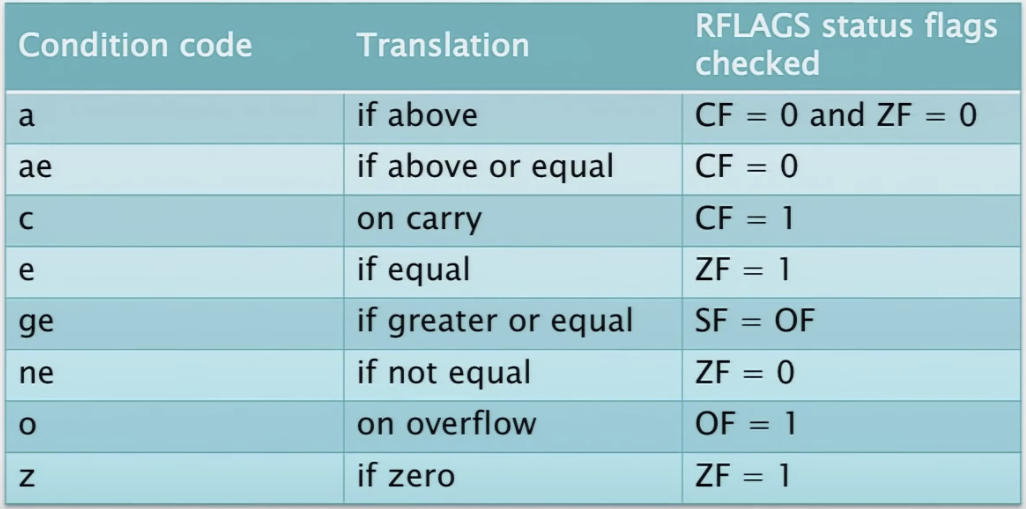
Q: Why do the condition codes e and ne check the zero flag?
A: Hardware typically compares integer operands using subtraction.
x86-64 Direct Addressing Modes
The operands of an instruction specify values using a variety of addressing modes.
- At most one operand may specify a memory address.
Direct addressing modes
- Immediate: Use the specified value.
movq $172, %rdi
- Register: Use the value in the speicified register
movq %rcx, %rdi
- Direct memory: Ues the value at the specified memory address
movq 0x172, %rdi
Q: How many cycles of the machine does it typically take to fetch something from memory these days? A: A coupel of hundreds. So clearly, if you can get things into registers, most registers you can access in a single cycle.
Indirect Addressing modes
The x86-64 ISA also supports indirect addressing: specifying a memory address by some computation
- Register Indirect: The address is stored in the specified register
movq (%rax), %rdi
- Register indexed: The address is a constant offset of the value in the specific register
movq 172(%rax), %rdi
- Instruction-pointer relative: The address is indexed relative to
%ripmovq 172(%rip), %rdi
Base Indexed Scale Displacement
The most general form of indirect addressing supported by x86-64 is the base indexed scale displacement mode.
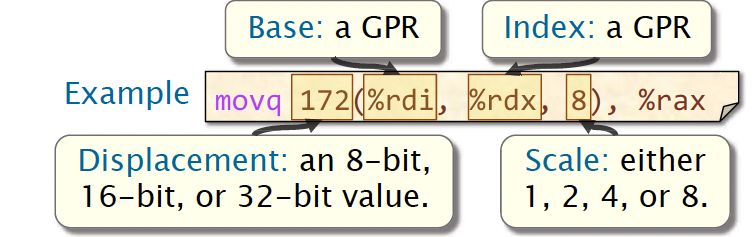
This mode refers to the address
Base + Index*Scale + Displacement
If unspecified, Index and Displacement default to 0, and Scale defaults to 1.
Jump Instructions
The x86-64 jump instructions, jmp and j<condition>, take a label as their operand, which identifies a location in the code.
- Lables can be symbols, exact addresses, or relative addresses.
- An indirect jump takes as its operand an indirect address.
jmp *%eax
// example from fib.s
jge LBB0_1
...
LBB0_1:
leaq -1(%rbx), %rdi
// example from objdump fib
jge 5 <_fib + 0x15>
...
15:
leaq -1(%rbx), %rdi
Assembly Idioms 1
The XOR opcode xor A, B computes the bitwise XOR of A and B. For example
Question: What does the following assembly do?
xor %rax, %rax
# zeors the register
Answer: Zeros the register
Assembly Idioms 2
The test opcode test A, B, computes the bitwise AND of A and B and discard the result, preserving the RFLAGS register. For example, the code snippets below checks to see whether the register is 0.
Question: What does the test instruction test for in the following assembly snippets?
test %rcx, %rcx
je 400c0a <mm+0xad> # jump to that address if %rcx holds 0
test %rax, %rax
cmovne %rax, %r8 # do the conditional move if %rax holds 0
Answer: Checks to see whether the register is 0.
Assembly Idioms 3
The x86-64 ISA includes several no-op (no operation) instructions, including nop, nop A (no-op with an argument), and data16.
Question: What does this line of assembly do?
data16 data16 data16 nopw %cs:0x0(%rax, %rax,1)
# the instruction does nothing!
Answer: Nothing!
Question: Why would the compiler generate assembly with these idioms? Answer: Mainly to optimize instruction memory (e.g., code size, alignment)
Floating-Point Instruction Sets
Modern x86-64 architectures support scalar (i.e., non-vector) floating-point arithmetic via a couple of different instruction sets
The original 8086 did not have a floating-point unit. Floating point was done in software. And then they made a companion chip that would do floating point and later was integrated to the CPU.
- The SSE and AVX Instructions support single-precision and double precision scalar floating-point arithmetic, i.e.,
floatanddouble - The x87 instructions support single-, double-, and extended-precision scalar floating-point arithmetic, i.e.,
float,double, andlong double.
The SSE and AVX instruction sets also include vector instructions.
Vector Instructions
Vector instructions generally operate in an elementwise fashion:
- The
ith element of one vector register can only take part in operations with theith element of the other vector registers - All lanes perfom exactly the same operation on their respective elements of the vector
- Depending on the architecture, vector memory operands might need to be aligned, meaning their address must be multiple of the vector width.
- Some architectures support cross-lane operations, such as inserting or extracting subsets of vector elements, permuting the vector, scatter, or gather.
Modern x86-64 architectures support multiple vector-instruction sets
- Modern SSE instruction sets support vector operations aon integer, single-precision, and double-precision floating-point values.
- The AVX instructions support vector operations on single-precision, and double-precision floating point values
- The AVX2 instructions add integer-vector operations to the AVX instruction sets
- The AVX-512 instructions increase the register length to 512 bits and priovide new vector operations, including popcound.
OVERVIEW OF COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE
A simple 5-stage processor
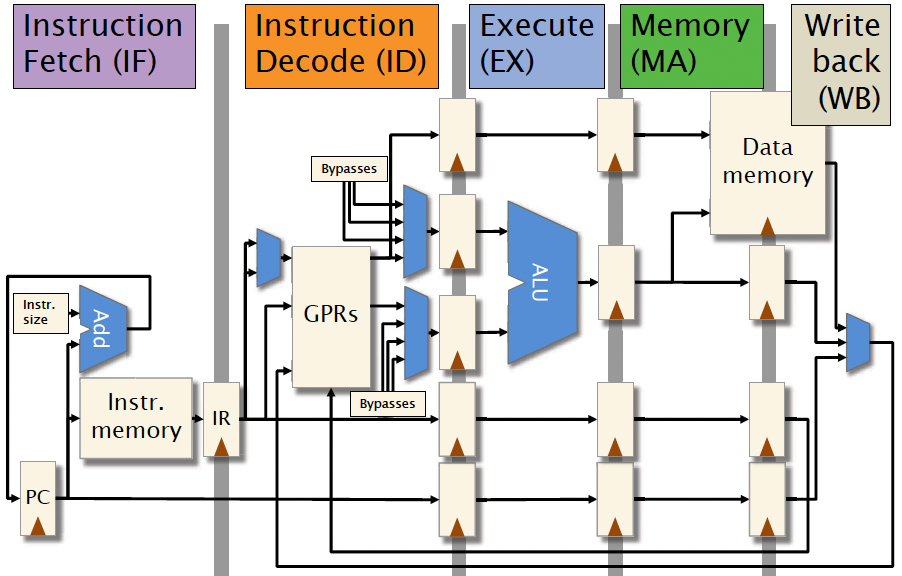
Block Diagram of 5-Stage Processor
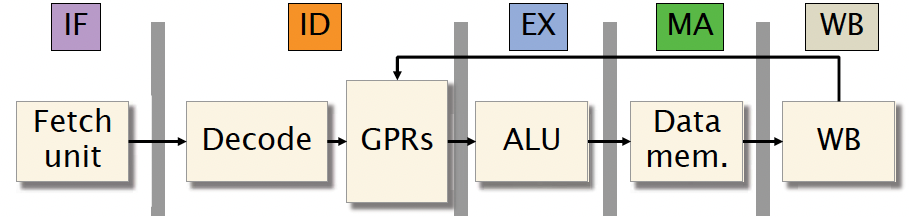
Each instruction is executed through 5 stages:
- Instruction fetch (IF): Read instruction from memory.
- Instruction decode (ID): Determine which units to use to execute the instruction, and extract the register arguments.
- Execute (EX): Perform ALU operations.
- Memory (MA): Read/write data memory.
- Write back (WB): Store result into registers.
Architectural Improvements
Historically, computer architects have aimed to improve processor performance by two means:
- Exploit parallelism by executing multiple instructions simultaneously.
- Examples: instruction-level parallelism(ILP), vectorization, multicore
- Exploit locality to minimize data movement.
- Example: caching.
